Our Cisco TelePresence endpoints are currently on TC6.0.1, while the latest being TC7.1.3. So I opened up TMS > Systems > System Upgrade > Software Manager; this is where we can upload the latest files to TMS, so the endpoints can download the updates easily.
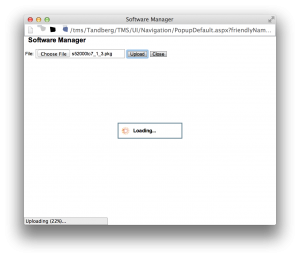
Now the problem is when you click “Upload New Software”, select the TC7.1.3 pkg file, and hit the Upload button.
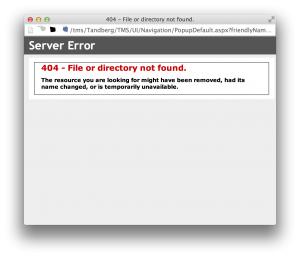
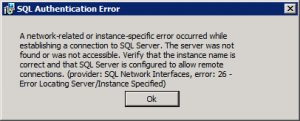
Everything looks fine, right until the upload reaches 100%. At that point, it’ll show: “Server Error – 404 – File or directory not found.”
The reason is that TMS only allows files that are ~300MB to be uploaded, and the TC7.1.3 pkg file is ~320MB… just a little bit over that upload limit.
The solution: Remote Desktop into the TMS server and edit the Web.config file, located at “C:\Program Files (x86)\TANDBERG\TMS\wwwTMS\”.
Find this line:
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="307200" executionTimeout="300" requestValidationMode="2.0" />And replace it with this line:
<httpRuntime maxRequestLength="512000" executionTimeout="300" requestValidationMode="2.0" />Then find this line:
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="314572800" />And replace it with this line:
<requestLimits maxAllowedContentLength="512572800" />This will increase the upload file size limit to ~500MB. Now restart IIS and the new limit will be used.
Tip: Copy the Web.config file to the Desktop and edit that copy. When finished editing, save it, drag it back into the wwwTMS folder, and click Replace file.